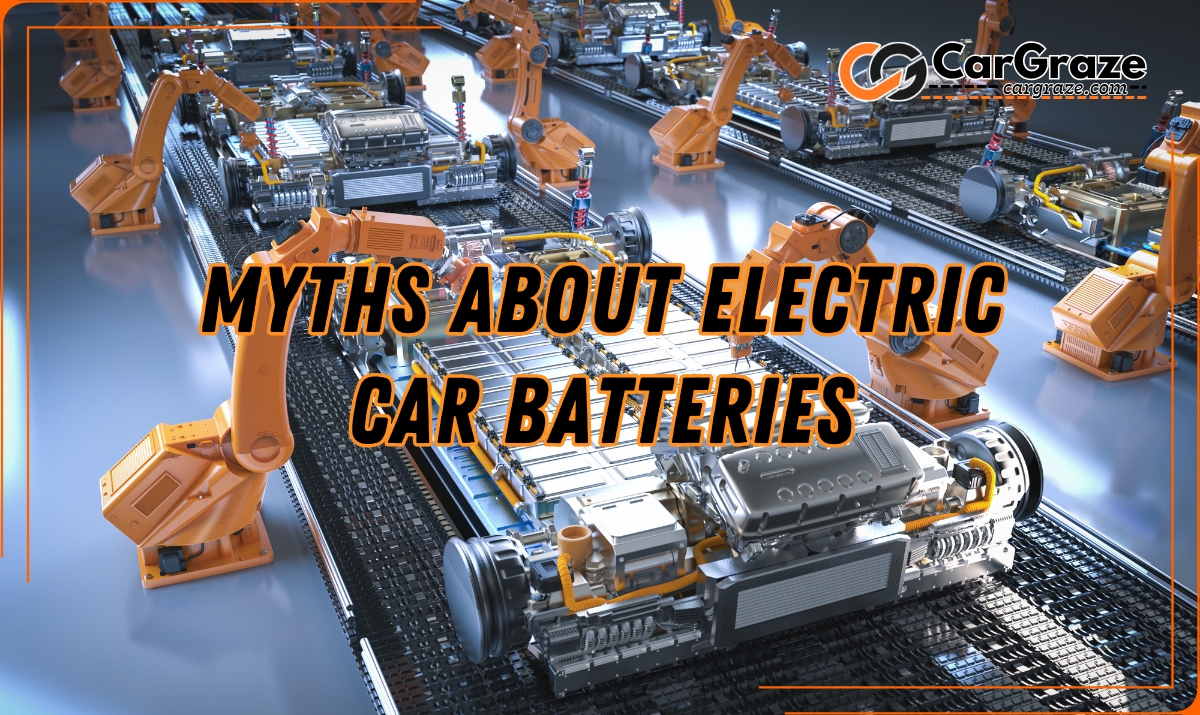
The Ultimate Guide to Electric Car Batteries: LFP vs. NMC and Everything in Between
If you're on the fence about whether to go electric, you're not alone. With so many options out there - petrol, diesel, CNG, hybrid, and electric - it's easy to feel overwhelmed. But today, let's zero in on one of the most critical components of an electric car: the battery.
In this post, we’ll break down the facts, debunk the myths, and give you all the info you need to make an informed decision about electric car batteries.
Types of Electric Car Batteries: LFP vs. NMC
Electric cars primarily use two types of batteries: LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) and NMC (Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide). But what’s the difference?
1. LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate)
- Brands that use it: Tata Motors, BYD, Volkswagen Group, and even Tesla (for standard-range models).
Key features:
- Longer lifespan with 2,500-3,000 charge cycles.
- Better chemical stability, means they’re less likely to overheat or degrade quickly.
- Slightly bulkier, requiring more space in the car.
2. NMC (Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide)
- Brands that use it: Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Hyundai, Kia, and Tesla (for high-end models).
Key features:
- Higher energy density means more power in a smaller size.
- Faster discharge rates, making them ideal for performance-oriented cars.
- Operates well in low temperatures.
Pros and Cons of LFP and NMC Batteries
Both battery types have their advantages, and neither is inherently "better." Here's a quick breakdown:
Advantages of NMC Batteries:
- Compact size: NMC batteries take up less space, allowing for more room in your car for storage or design flexibility.
- Performance-friendly: They deliver faster discharge rates, making them perfect for sporty, high-performance EVs.
- Low-temperature efficiency: NMC batteries handle cold climates better.
Advantages of LFP Batteries:
- Longer lifespan: With more charge cycles, these batteries last longer, reducing the need for replacements.
- Stability: LFP batteries are more chemically stable, which means fewer chances of overheating or thermal runaway.
- Cost-effective: While slightly bulkier, advancements like blade technology have made them more efficient and compact over time.
Busting Myths About Electric Car Batteries
Myth #1: Electric cars catch fire easily.
Reality check: Electric cars are statistically less likely to catch fire than traditional petrol or hybrid vehicles. For every 100,000 EVs sold, only 25 incidents of fires are reported, compared to 1,529 for petrol cars and 3,474 for hybrids.
Why? EVs don’t rely on combustion to run. Their batteries are equipped with sophisticated cooling systems to prevent overheating, making thermal runaway highly unlikely.
Myth #2: EV batteries don’t last long.
Truth: Most EVs come with warranties of 8 years or 160,000 km, and in real-world scenarios, batteries can last much longer. For example, a Tesla Model S owner clocked over 1.6 million kilometres, with the original battery running for 1.2 million of those!
Here’s the math:
- If an EV has a range of 300 km per charge and 1,500 charge cycles, the battery could last up to 450,000 km.
- Even if you drive 100 km daily, that’s over 12 years of battery life!
Are Electric Cars Worth It?
Let’s crunch some numbers. The running cost of an EV is around ₹1–1.5 per km, while petrol cars cost ₹10–12 per km. Over 300,000 km, you could save around ₹30 lakh in fuel costs - enough to cover the car's cost multiple times!
Plus, with the advancements in battery technology and government incentives for EV adoption, the long-term benefits far outweigh the initial investment.
What About Battery Replacement Costs?
A common concern is: What happens after the warranty ends?
- First, most EVs come with robust warranties of 8 years or 160,000 km.
- Second, even after the warranty period, batteries typically degrade gradually.
- For instance, after 320,000 km, a Tesla's battery may still retain 88% of its capacity, giving you ample usability.
Final Thoughts: LFP or NMC?
Both LFP and NMC batteries are reliable, and the choice often depends on your priorities:
- Want a longer-lasting battery with better stability? Go for LFP.
- Need higher performance in a compact package? Choose NMC.
No matter your choice, switching to an electric vehicle is a smart, sustainable move for the future. With lower running costs, improved technology, and growing infrastructure, there’s never been a better time to go electric.


Comments